Leadership is an influence process, working with people to accomplish their goals and the organisations goals.
Positive leadership traits are.
- Good people connections
- Clear vision
- Ability to develop connections with check in and monitor.
- Support and develop individuals to utilise their strengths.
- Create casual catchups
- Be crave
- Inspires team to create vision and communicate how that relates to each team member.
- Create a great culture
- Celebrate success.
With your check ins you want to adapt these as required for each team member based on their tasks. Consider if this is a new task for them, where are they on the learning journey, where in their competency level. How committed and enthusiastic are they?
Situational leadership is a mix of directional (task and supervisor) / management ‘ sociology emotional support / development level that improves the team.
A good tool to check out is Gilberts 6 windows as illustrated here.
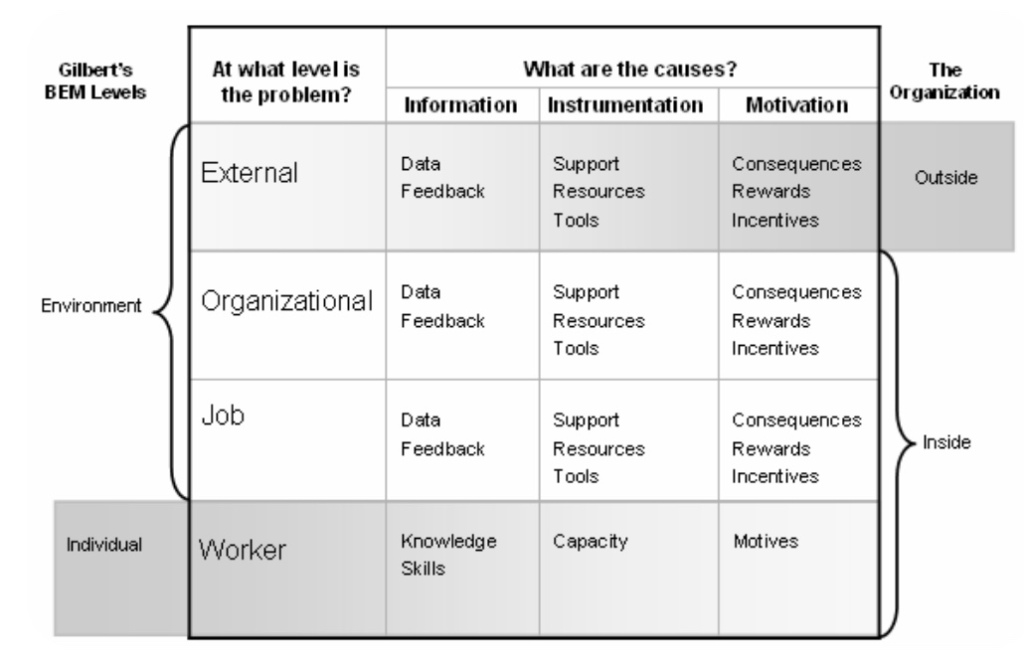
- Information cause. This is the enthusiastic beginner stage, Telling. Define standards, go step by step, monitor results and have short review timeframes. Understand what does a good job look like. Get a clear goal and when it needs to be done by.
- Instrumental cause. Disillusioned learner. – selling . Provide standards, support and praise to build confidence, coach and involve in decision making. Help them answer if they are on the right track and why it’s important.
- Capacity cause. Capable but cautious performer. Participating. Support with feedback and positive reinforcement. Praise, listen and facilitate. Build trust you have their back. Listen to their ideas and remind them of what they do well.
- Motives cause. Self reliant achiever / delegating. Communicate objective and allow them the responsibility. Checkin and provide positive reinforcement. Allow them the freedom to innovate and to come up with new ideas and choose their work.
When implementing change think about the positive reinforcement and negative consequences to action. Ensure you observe and catch the positive behaviour and reinforce it. Assume everyone wants to do a good job.
Positive reinforcement must be valued by the performer.
Consequences can be positive or negative, immediate or in the future, certain or uncertain. these factors greatly impact the behaviour.
When leading a team think about creating person profiles for your people. Include the following information:
- What they are working on
- What they are good at.
- Who they have good connections with
- How do they like feedback.
- How they like to be appreciated
- How they learn
- What their values are
- Look at the Gilbert windows above.
- Family status (for small talk and rapport building.)
- Hobbies
- Any known issues
- Major milestone (birthdays, house move, marriage, kids etc )
- Home location and travel issues.
When thinking about feedback styles you can use the STAR method.
- Situation or task – when this happened….
- Action – you did this….
- Result –
- Alternative action – what you could have done was….
- Alternative result – this might result in……
Or. DESC method.
- Describe the problem or issue
- Empathise with them and express how you feel
- Specify what you want to happen
- Consequences positive and negative.
Some reflection techniques.
3W’s
- What went well.
- What didn’t go so well
- What might you do differently next time.
4 F’s
- Focus on facts – what exactly happened and who was involved.
- Focus on self – how do you feel about this, what do you think you did well,
- Effect – what do you think is the knock on to others involved in the process and how might this affect your colleagues
- Future – how will you handle it next time.
STOP/ START/ KEEP
- What do you need to stop doing.
- What do you need to start doing
- What do you need to keep doing.
